As we age, maintaining muscle strength becomes increasingly challenging. Sarcopenia, the gradual loss of muscle mass and function, affects many adults over 60, making everyday activities like carrying groceries or climbing stairs feel harder. This can impact mobility, balance, and overall independence. Protein plays a key role in supporting muscle health, but not all sources provide the same benefits.
What if a familiar, creamy food could offer more protein per serving than eggs, along with additional nutrients for seniors? Greek yogurt stands out for its higher protein content and unique properties. In this article, we’ll explore how it compares to eggs and why it might fit well into a balanced diet for older adults.

Understanding Sarcopenia and the Role of Protein
Sarcopenia affects 10-16% of older adults worldwide, with higher rates in those over 80. It contributes to weakness, increased fall risk, and reduced quality of life. Research shows that adequate protein intake supports muscle maintenance, especially when combined with light activity.
Older adults often need 1.0-1.2 grams of protein per kilogram of body weight daily—more than younger people—to help counteract muscle changes. Distributing protein evenly across meals is beneficial.
Greek Yogurt vs. Eggs: A Quick Comparison
Greek yogurt is strained to remove whey, making it thicker and more concentrated in protein. Here’s how it stacks up against eggs:
| Food | Protein per 100g (approx.) | Key Notes for Seniors |
|---|---|---|
| Greek Yogurt (plain, nonfat) | 10-20g | Slow-digesting casein, probiotics, calcium |
| Eggs (two large) | 12g | Fast-digesting, nutrient-dense |
Greek yogurt often provides more protein per serving, plus gut-friendly probiotics that aid nutrient absorption—an important consideration as digestion can change with age.
Why Greek Yogurt Supports Muscle Health
Slow-Digesting Protein for Steady Support
Greek yogurt contains mostly casein protein, which digests slowly and releases amino acids over time. This can provide ongoing support for muscles, especially overnight. Studies indicate that slow-release proteins help maintain muscle protein synthesis in older adults.
Rich in Leucine for Muscle Repair
Leucine is key for triggering muscle protein synthesis. Greek yogurt offers a good amount, helping with recovery after daily activities or light exercise.
Additional Nutrients for Overall Well-Being
- Calcium → Supports bone health alongside muscles.
- Probiotics → Promote gut health, which can improve nutrient uptake.
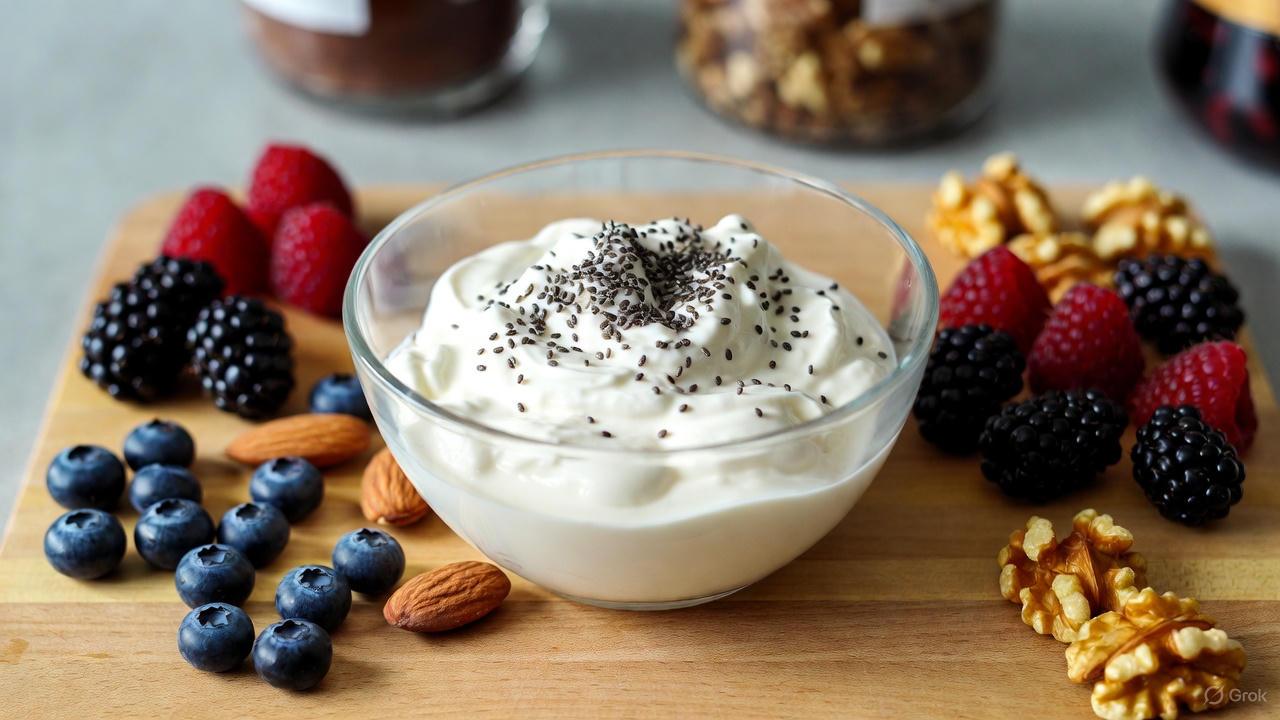

Actionable Ways to Include Greek Yogurt in Your Routine
Start small and build up. Aim for plain, unsweetened varieties to avoid added sugars.
- Morning Routine Try ¾ cup plain Greek yogurt with fresh berries or a sprinkle of nuts for a protein-packed start.
- Midday Snack Mix with chia seeds for extra fiber and texture.
- Evening Option Have a small serving before bed to support overnight muscle maintenance.
If you’re new to dairy, begin with smaller portions and choose lactose-free if needed. Pair it with light activity like walking or chair exercises for best results.

FAQ
How much Greek yogurt should I eat daily for muscle support? Aim for 1-2 servings (about ¾-1 cup each) as part of balanced meals. Combine with other protein sources for variety.
Is Greek yogurt suitable if I have lactose concerns? Many tolerate it well due to fermentation reducing lactose. Opt for lactose-free versions if sensitive.
Can I use Greek yogurt if I’m on medication? It’s generally safe, but consult your doctor, especially with digestive conditions or certain meds.
Final Thoughts
Greek yogurt offers a convenient, tasty way to boost protein intake, with benefits that go beyond eggs in protein density and added nutrients. Incorporating it thoughtfully can support muscle health as part of a well-rounded lifestyle.
This article is for informational purposes only and not a substitute for professional medical advice—consult your healthcare provider for personalized guidance.