It’s a frustrating reality many of us face as we get older: that slow, silent decline in physical strength, the feeling that your muscles are simply softening and disappearing, making everyday tasks feel heavier. This natural but accelerating process, scientifically known as sarcopenia, isn’t just about looking less toned; it steals your independence, increases your risk of falls, and fundamentally lowers your quality of life. You deserve to feel strong and capable at any age, not weakened by a condition you feel powerless to stop. The good news is that stopping this decline doesn’t require hours in the gym or drastic diet changes, but rather a simple, single-spoon ritual with a powerful, yet often overlooked, food every night.
The Silent Thief: Understanding Sarcopenia
The image of muscle loss is often subtle at first—maybe it’s just struggling to open a jar or finding the stairs a bit more tiring. But here’s the cold, hard truth: by the time you reach your 70s, you may have lost up to 50% of your total muscle mass compared to your younger years. This is not just cosmetic; it deeply affects your metabolism and overall health.
Why Your Muscles Shrink (And Why Diet is Key)
Many people assume this decline is purely due to age or lack of exercise. But the truth is far more complex: your body’s ability to process and utilize protein changes dramatically as you age. Your muscles become “anabolically resistant,” meaning they struggle to build and repair themselves, even when you eat the recommended amount of protein.
Here are the primary culprits behind muscle loss:
- Hormonal Shifts: Declines in hormones like testosterone and growth hormone make muscle maintenance tougher.
- Inflammation: Chronic, low-grade inflammation interferes with muscle repair signals.
- Protein Synthesis Trouble: The older gut and muscle tissue become less efficient at using the protein you consume.
The Problem With ‘Standard’ Protein
Many seniors try to compensate for muscle loss by eating more protein, like a piece of chicken at dinner. But here’s the kicker: research shows that simply eating a large amount of protein in one meal isn’t enough. Your muscles need a steady, highly bioavailable stream of specific building blocks, especially at a time when your body is naturally primed for repair: while you sleep.
The Surprising Power of Casein: Your Nighttime Muscle Shield
This is the exciting part. The superfood we’re talking about is not some expensive, exotic berry, but a specific type of protein: Casein Protein. While whey protein is quickly absorbed, making it ideal after a workout, casein is a slow-digesting protein, earning it the nickname “time-released” protein.
How Casein Works While You Rest
Imagine a small, steady drip feeding your thirsty muscles the nutrients they need over many hours. Well, that’s exactly what happens. Casein forms a gel-like structure in your stomach, slowing down its digestion and the release of amino acids into your bloodstream for up to 7-8 hours.
This sustained release does two incredible things:
- Prevents Catabolism: It dramatically reduces muscle breakdown (catabolism) that naturally occurs during your overnight fast.
- Fuels Repair: It provides a constant supply of essential amino acids, particularly Leucine, which is the crucial trigger for muscle protein synthesis (the rebuilding process).
This is why a single spoon of casein protein powder, mixed into a drink or yogurt before bed, can be a game-changer for older adults.
Beyond the Spoon: Maximizing Muscle Health
But that’s not all you need to know. While the nightly spoon of casein is essential, you can amplify its effects with a few other simple lifestyle tweaks. Maintaining strong muscles requires a comprehensive approach that tackles nutrition, movement, and recovery.
The Amino Acid Difference: Casein vs. Whey
To appreciate the “why” behind the nighttime ritual, it helps to see the difference between the two most common dairy-derived proteins:
| Feature | Casein Protein | Whey Protein |
| Digestion Speed | Slow (6-8 hours) | Fast (1-2 hours) |
| Best Time to Use | Before Bed or Between Meals | Post-Workout |
| Primary Benefit | Anti-Catabolic (Prevents Breakdown) | Anabolic (Rapid Building) |
| Texture | Thicker, creamier | Thinner, lighter |
Therefore, the secret lies in timing: Whey for immediate recovery, Casein for overnight maintenance.
Simple Movements to “Wake Up” Your Muscles
The protein is the fuel, but movement is the spark plug. Sarcopenia doesn’t respond well to inactivity. You don’t need to lift heavy weights to see results; simple resistance training can prime your muscles to better use the protein you consume.
- Bodyweight Squats: Do 3 sets of 10 while holding onto a chair for balance.
- Wall Push-ups: Perform 3 sets of 12 against a wall to build upper body strength safely.
- Band Rows: Use a simple resistance band to pull and work your back and shoulders.
Even 15-20 minutes of light resistance work, three times a week, can drastically improve your body’s ability to retain and build new muscle tissue. This is the synergy you’re looking for.
Your Actionable 7-Day Strength Plan
You can start implementing this muscle-saving strategy tonight. Here are the simple, concrete steps you can follow immediately.
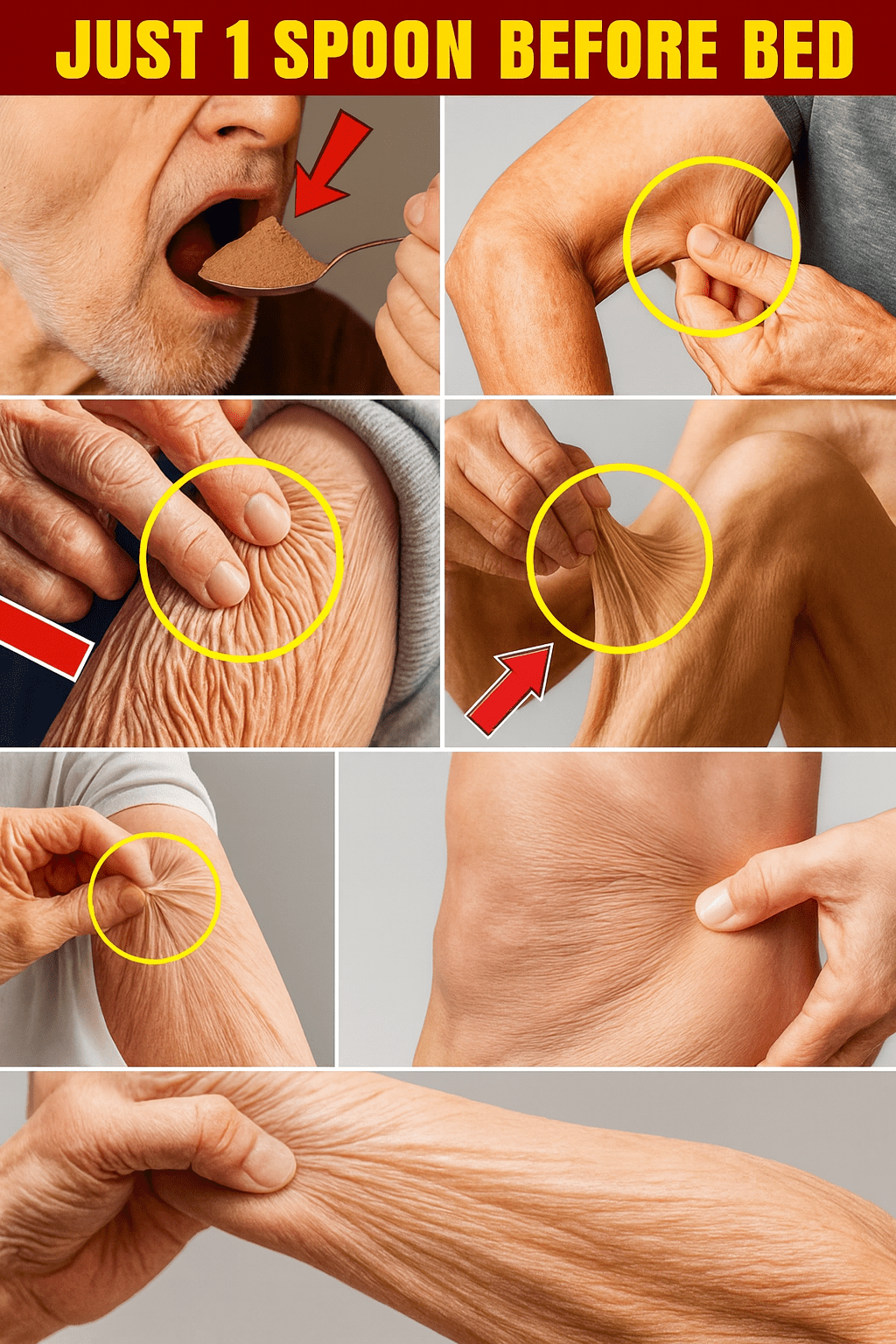
Step 1: Secure Your Superfood
Purchase a high-quality Micellar Casein Protein powder. Avoid brands with excessive sugars or artificial ingredients. Look for products that specifically state “Micellar Casein.”
Step 2: Master the Nighttime Routine
Mix one (1) tablespoon (about 15-20 grams) of casein protein powder with a small glass of water, almond milk, or blend it into a small portion of Greek yogurt. Consume this 30-45 minutes before you go to sleep. This timing ensures the slow-release effect kicks in optimally during your deepest sleep cycles.
Step 3: Hydrate to Activate
Protein metabolism requires water. Make sure you drink at least 8 glasses of water throughout the day. Without sufficient hydration, your body struggles to utilize protein effectively.
Step 4: Prioritize Leucine-Rich Daytime Meals
While casein works its magic at night, make sure your daytime meals include high-leucine sources to further trigger muscle growth. Foods rich in this essential amino acid include:
- Chicken and turkey breast
- Tofu and soybeans
- Cottage cheese and Greek yogurt
- Lentils
The Leucine Secret Revealed
Here’s the exciting secret promised at the beginning: Casein is particularly potent because it is a complete protein, rich in all nine essential amino acids, including a very high concentration of Leucine. Leucine is not just a building block; it acts like a signaling switch. It literally tells your muscle cells, “Start building!” By feeding your body this high-quality, slow-release Leucine source right before your longest fasting period, you are effectively keeping that “building” signal active throughout the night, drastically reducing the net muscle loss. This simple spoonful is the most efficient way to maximize your muscle-building window every 24 hours.
Conclusion: Reclaiming Your Strength
It’s clear that halting the shrinking muscle phenomenon is not about luck; it’s about strategic nutrition and movement. By adopting the simple nightly habit of one spoon of casein protein, coupled with smart, consistent light resistance exercise, you can give your body the tools it needs to prevent catabolism and enhance overnight repair. Don’t let sarcopenia dictate your future. Take control of your strength and vitality starting tonight.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: Is Casein safe for people with lactose intolerance?
A: Casein is a milk protein, and while it contains very little lactose, pure casein powder can still cause issues for those with severe lactose intolerance. However, it often causes fewer digestive problems than standard milk. Always start with a half-dose to test your tolerance, or opt for high-quality plant-based protein powders (like pea or soy isolate) as an alternative, though their slow-release benefits may not be as pronounced as micellar casein.
Q2: Can I just eat cottage cheese instead of a protein powder?
A: Yes, absolutely! Cottage cheese is naturally high in casein and is an excellent, whole-food alternative. A half-cup of low-fat cottage cheese contains about 14 grams of protein, mostly casein. This is a highly recommended and delicious option for your nighttime ritual. The powder is simply a more concentrated and convenient option.
Q3: When should I take my casein if I exercise in the evening?
A: If you work out in the late afternoon or evening, you should first prioritize a fast-digesting protein (like whey or a plant-based alternative) immediately after your workout. Then, wait 1-2 hours after that recovery meal, and take your casein protein 30-45 minutes before bed. This ensures you get the immediate repair benefits from the post-workout protein and the sustained anti-catabolic benefits from the nighttime casein.
Medical Disclaimer
The information presented in this article is for educational purposes only and is not intended as a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of your physician or another qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition or before making any dietary or lifestyle changes.