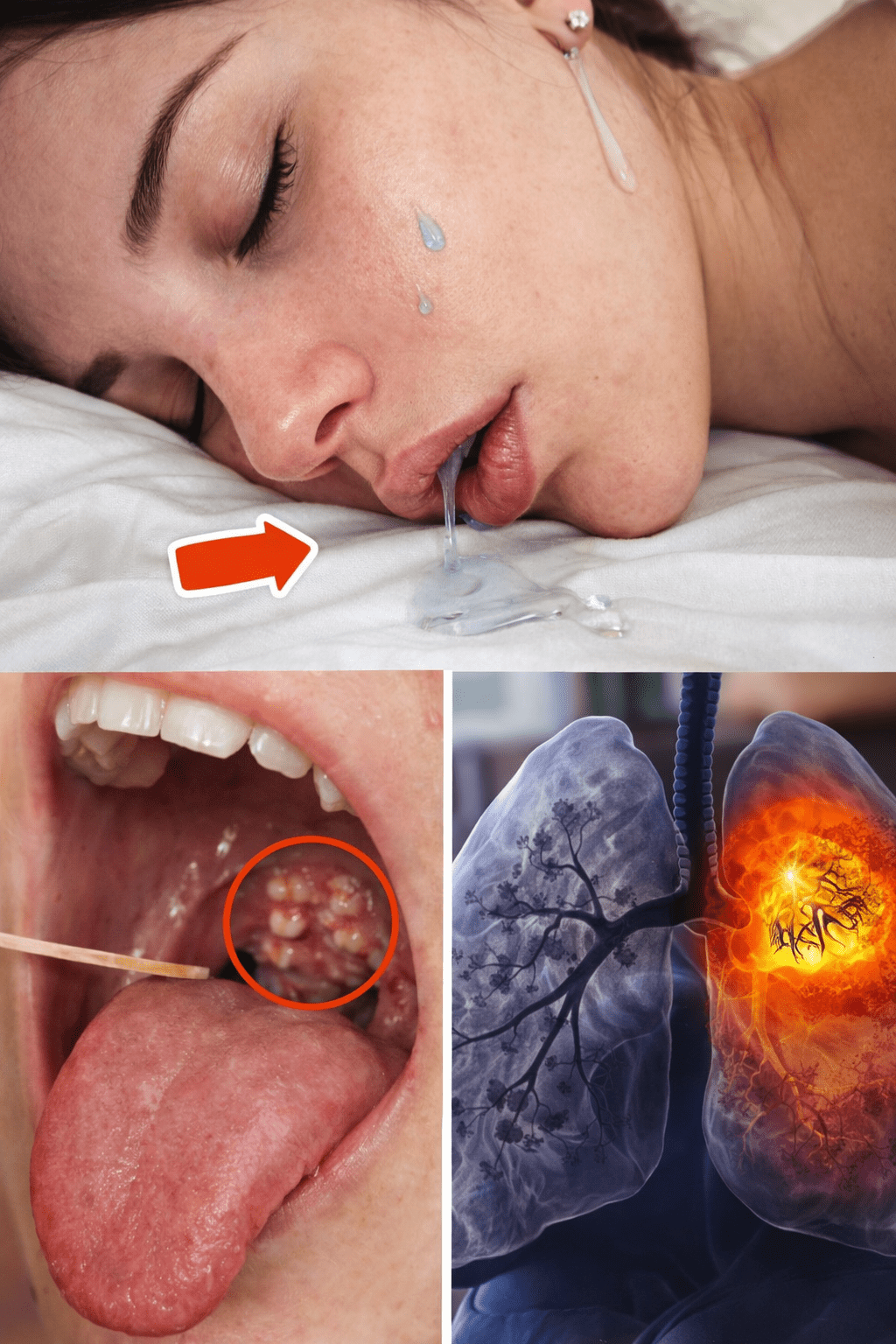
Waking up with a damp pillow can feel embarrassing and uncomfortable. Many people experience this from time to time, and it often leaves them wondering what’s going on with their body during the night. The frustration builds when it happens repeatedly, disrupting your morning routine and even affecting how rested you feel.
But here’s the good news: understanding the possible reasons behind it can help you take simple steps to manage it. And by the end of this article, you’ll discover some practical insights that might surprise you and encourage you to pay closer attention to your sleep habits.
Understanding Drooling During Sleep
Drooling while asleep, also known as sialorrhea at night, happens when excess saliva escapes your mouth. Your body produces saliva continuously to keep your mouth moist and aid digestion. During deep sleep, swallowing slows down, and if your mouth is open, saliva can pool and drip out.
Most of the time, this is harmless and tied to everyday factors. However, research shows that persistent drooling can sometimes link to other health aspects worth monitoring.
8 Common Reasons You Might Drool While Sleeping
Let’s break down the most frequently mentioned factors. Keep in mind that everyone is different, and what applies to one person may not to another.
1. Your Sleeping Position
Side or stomach sleeping allows gravity to pull saliva out more easily. Back sleeping tends to keep it inside.
Studies indicate that changing positions can reduce this issue for many people.
2. Nasal Congestion or Allergies
When your nose is blocked from colds, allergies, or sinus problems, you breathe through your mouth. This opens the door for saliva to escape.
Clearing your airways before bed often helps.
3. Sleep Apnea
This common sleep disorder causes pauses in breathing, leading to mouth breathing and more drooling. Loud snoring, daytime tiredness, and morning headaches are other signs.
Research from sleep experts links untreated sleep apnea to various nighttime symptoms, including excess saliva flow.
4. Acid Reflux (GERD)
Gastroesophageal reflux happens when stomach acid flows back up, irritating the throat and triggering extra saliva production as a protective response.
Nighttime episodes are common when lying down, and studies show this can contribute to drooling.
5. Infections or Throat Irritation
Tonsillitis, strep throat, or sinus infections can swell tissues, making swallowing harder and increasing saliva buildup.
These usually resolve as the infection clears.
6. Certain Medications
Some drugs, like those for mental health or neurological issues, list increased salivation as a side effect.
If you suspect this, discussing alternatives with your doctor might help.

7. Neurological Conditions
In some cases, conditions like Parkinson’s disease or stroke affect muscle control around the mouth, leading to difficulty swallowing saliva.
Research highlights this as a factor in chronic cases.
8. Teeth Grinding (Bruxism)
Grinding at night can stimulate saliva glands or cause mouth breathing.
Wearing a night guard sometimes reduces both grinding and drooling.
But that’s not all—there are everyday habits that can make a big difference too.
Simple Habits to Help Reduce Nighttime Drooling
You don’t have to live with it. Here are actionable steps many people find helpful:
- Try sleeping on your back with a supportive pillow to elevate your head slightly.
- Use a humidifier or saline spray to keep nasal passages clear.
- Avoid heavy, spicy meals close to bedtime.
- Stay hydrated during the day but taper off liquids before sleep.
- Practice good oral hygiene to minimize irritation.
Here’s a quick comparison of common triggers and tips:
| Trigger | Why It Happens | Practical Tip |
|---|---|---|
| Sleeping Position | Gravity pulls saliva out | Switch to back sleeping |
| Nasal Congestion | Forces mouth breathing | Clear sinuses before bed |
| Acid Reflux | Extra saliva to neutralize acid | Eat earlier, elevate head |
| Sleep Apnea | Airway issues lead to mouth breathing | Monitor for snoring and fatigue |
And another list of red flags that suggest chatting with a doctor:
- Frequent loud snoring or gasping at night
- Persistent daytime sleepiness
- Ongoing heartburn or throat pain
- Sudden changes in drooling patterns
- Difficulty swallowing during the day
The truth is, addressing these early can improve your sleep quality significantly.
When to Consider Professional Advice
Occasional drooling is normal for most adults. But if it’s excessive, frequent, or accompanied by other symptoms like chronic fatigue or breathing issues, it’s wise to consult a healthcare provider.
They can help rule out underlying factors and suggest personalized approaches.

Conclusion
Drooling while sleeping affects many people and often stems from simple, manageable causes like position or congestion. By tuning into your body’s signals and trying small changes, you can often reduce it and wake up feeling fresher.
Remember, better awareness leads to better nights—and that’s something worth aiming for.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is drooling while sleeping normal?
Yes, for many people it’s occasional and harmless, especially during deep sleep when swallowing slows.
Can drooling indicate sleep apnea?
It can be one sign, particularly with mouth breathing, but other symptoms like snoring are key indicators.
How can I stop drooling at night naturally?
Start with back sleeping, clearing your nose, and avoiding late meals—many see improvement quickly.
Disclaimer: This article is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice. If you have concerns about drooling or related symptoms, please consult a healthcare provider for personalized guidance.